
Contents
What is Video Encoding?
Video encoding, also known as video compression, is the process of converting raw video data into digital images by using a specific codec. During this process, unnecessary or redundant information will be intelligently removed from the raw file and converted to a much smaller file, thus making it easier to store and transmit over networks.
Common Encoding Concepts
1. Codec
A codec is a specific algorithm used to compress and decompress raw video sources. Some popular codecs are H.264, H.265, and VP9. The compression and decompression should be always in the same codec.
2 . Bit Rate
The bit rate is the amount of data processed per unit of time in the raw video source. A higher bit rate generally results in higher-quality video but also increases the file size accordingly.
3. Frame Rate
Frame rate is the number of frames displayed per second in a video. Common frame rates include 7, 12, 24, 25, 30, and 60 frames per second for security CCTV cameras.
4. Resolution
Resolution pertains to the pixel count in two dimensions. Typically, resolution remains unchanged before and after decoding. However, for specific purposes, it may be adjusted during encoding to accommodate different devices or bandwidth, a process known as transcoding.
5. Aspect Ratio
The aspect ratio represents the width-to-height ratio of a video, with common ratios being 4:3 and 16:9. It can be adjusted while encoding to match various screens, also called transcoding.
6 - Group of Pictures Structure
The GOP structure, short for Group of Pictures, arranges frames into the following hierarchy:
- I-frames, also known as Key Frames
- P-frames, also known as Predicted Frames
- B-frames, also known as Bi-predictive Frames
This organisation defines the GOP structure. The GOP process generally enhances compression efficiency. However, during decoding, it's crucial to use the correct GOP value to ensure accurate decoding.
Through video encoding, the large raw video files are transformed into compact and lightweight formats without significantly compromising the visual quality, thus facilitating a wider and more efficient transmission and storage of videos. We can summarise the benefits of video encoding into three main points:
1. Reduced File Size: Video encoding simplifies storage and transmission by reducing file sizes.
2 . Optimised Streaming: Video encoding enables smoother streaming, reducing buffering and lowering bandwidth demands.
3. Compatibility: Video encoding allows adaptation to various device and platform specifications, such as different resolutions or bitrates, ensuring compatibility.
What is Video Decoding?
Video decoding is the process of converting a compressed or encoded video file back to its original uncompressed format so that it can be played on a video player. This article will provide a detailed breakdown of the process and the key concepts involved.
Common Decoding Concepts
1. Codec
A codec plays a crucial role in decoding because it represents the specific method or program employed for the initial video encoding. When decoding, the decoder employs the same codec to restore the file to its original state.
2. Bitstream
The encoded video file, also known as a bitstream, contains compressed data that needs to be unpacked. The decoder reads this bitstream and begins the process of reconstructing the video data.
During decoding, the individual frames are reconstructed based on the information available in the compressed file. The decoder uses reference frames to rebuild the other frames (P-frames and B-frames) in the Group of Pictures (GOP) structure.
4. Buffering
To ensure smooth playback, a buffer temporarily stores decoded video data before it is displayed. If the buffer is empty, you may experience lag or buffering during playback.
5. Rendering
After the video data undergoes decoding, it gets forwarded to the renderer. The renderer's role is to display the frames on the screen, essentially reconstructing the moving pictures as they were originally captured.
6. Audio Synchronization
Decoding encompasses more than video processing; it also entails the synchronisation of the audio stream with the video, ensuring precise alignment for a unified and seamless viewing and auditory experience.
7. Output the data
The final step is to output the decoded data to a video player, ex: Nx Desktop Client, Mobile client, or the video data handler for further processing, such as Video analytics applications.
In summary, video decoding is an intricate process that restores compressed video data, including both audio and video, to its original state. It plays a critical role in the video display process.
Comparing Software and Hardware Video Decoding
Video decoding can be accomplished through two approaches: software and hardware, each with its unique advantages.
In software decoding, the CPU oversees the decoding process and video playback. This method excels in flexibility, as it supports a wide range of stream formats and can adapt easily to new ones through application updates. This adaptability proves particularly valuable when dealing with uncommon stream formats or expanding codec compatibility.
In contrast, hardware decoding delegates all tasks to a specialised chip, typically the GPU, which boasts numerous cores dedicated to this specific task and can process tasks in parallel. The most significant advantage is that it relieves the CPU of the decoding workload, allowing it to handle other system tasks and ensuring system responsiveness, especially during resource-intensive operations.
When do we need Hardware Decoding?
Nx Desktop is an extremely lightweight application that demands minimal hardware resources, making it compatible with standard onboard graphics in most situations. However, it is advisable to utilise a GPU in the following scenarios:
-
When multiple video playback instances with high resolution and/or high frame rates are necessary.
-
When the Desktop Client operates on a lower-spec or low-power CPU, such as Intel Atom or Celeron.
-
When the Desktop Client runs on a computer handling multiple tasks concurrently.
Hardware Acceleration for Nx Witness Desktop client
Nx Witness Desktop now offers support for Intel® Quick Sync Video. To determine if your Intel processor is compatible with Quick Sync Video, please refer to the product specification page of your processor. To activate hardware acceleration in the Nx Witness Desktop client, follow the steps below:
-
Open the Main Menu.
-
Navigate to Local Settings.
-
Go to the Advanced section.
-
Check the box labeled "Use Hardware Video Decoding."
-
Click Apply to save your changes.
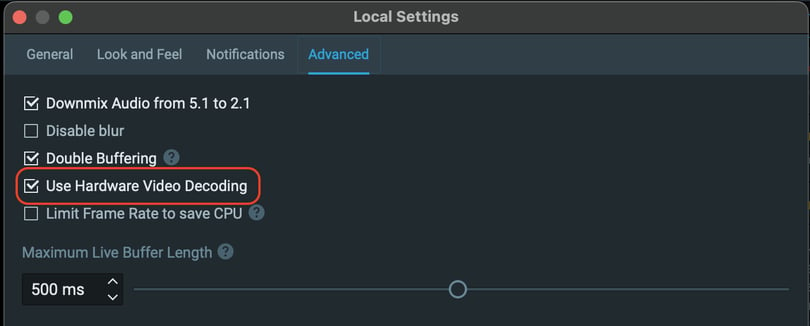
Please note that the video item must be removed from the Layout and added back for this change to take effect. Furthermore, if the computer has more than one GPU, the Intel GPU needs to be the "primary display" to enable hardware decoding.
2. Advanced Mapping Solution: Navicops Works With Nx
Navicops enables intelligent map creation in Nx Witness by incorporating images, PDFs, and Bing satellite maps within the Nx client. Access, navigate, and manage devices, I/O sensors, Soft Triggers, and Maps seamlessly. This seamless integration streamlines workflows by providing intelligent maps, efficient device monitoring, and real-time insights within Nx Witness. Conveniently oversee IP devices, access recorded images, and check device statuses within the familiar interface.
Key Features
- Create Intelligent Maps: Utilise various elements, including images, PDFs, and Bing satellite maps, to create interactive maps that offer a clear overview of your surveillance environment.
- Smarten Your Installation: Add and control I/O sensors, Soft Triggers, and web pages directly on your maps for efficient management.
- Oversee IP Devices: Monitor your IP devices effortlessly through a user-friendly dashboard and a dedicated web page for system management, ensuring installation stability.
- Intuitive Interface: Enjoy an intuitive interface that simplifies control and management, providing easy access to the latest recorded images, map links, previews, and device statuses.
- Supervision Interface: Cross-reference information and monitor the status of diverse devices to promptly identify and address any issues within your installation.
To organise a Navicops mapping demo for your team contact jlahnstein@networkoptix.com
3. Dell Technologies Storage Solutions for Nx Witness VMS
Dell Technologies has recently released comprehensive guides for sizing and configuring their storage solutions in collaboration with Nx Witness VMS. These guides provide insights into the best practices and recommendations for integrating Dell storage with Nx Witness VMS. Access and download these guides here.
4. Freeway Wholesalers Launch New Website
Freeway Wholesalers has just launched a state-of-the-art website, providing a hub for all your security needs. Explore the industry's latest innovations, such as Nx Witness v5.1, and other top-notch products that safeguard what matters most to you. Head over to the website today to stay connected with the team at Freeway. https://www.freewaysecurity.com.au/

5. Win a Weber Q at the VSP Experience Centre!
Join the Nx Team on October 12th from 4 to 6 PM for a special event to mark the opening of the new VSP QLD experience centre. The launch event will feature door prizes, including a Weber Q, PS5, and Samsung ULED TV, making it an enjoyable evening to remember. Scan the QR code in the image below to register. We look forward to seeing you there!
Date: Thursday, 12th October
Time: 4PM - 6PM
Location: 1/14 Indy Ct, Carrara QLD 4211




